It was the end of 2022, exactly two years ago. My last project had failed, and I was left feeling hopeless and deeply disappointed.
I couldn’t figure out what I kept doing wrong or why everything I built kept falling apart
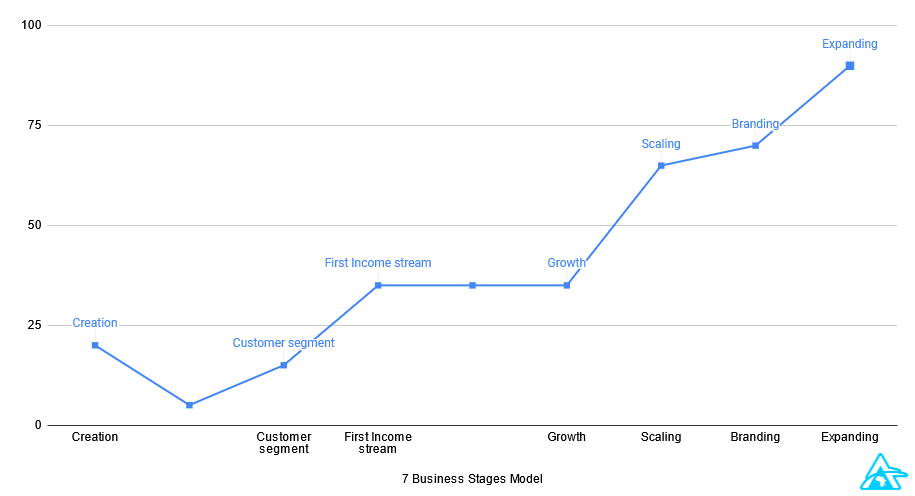
Out of necessity, I sat down and created the 7 Business Stages Model.
That model became the most helpful thing I’ve ever done. It gave me clarity. It made me focus on the right thing, at the right time.
That’s when I knew I had to share it with others. Entrepreneurs who feel stuck, lost, or unsure of what to do next.
If you’re building a business and feel like you’re running in circles, this model can guide you the same way it guided me.
Let’s go through each stage so you can see how it all fits together.
The goal of this model
When building a business, many people, just like I did, focus too much on the big goal, and that can get overwhelming.
It usually leads to confusion and lack of direction, and before you know it, you’re stuck in the same place, just running in circles.
The goal of this model is to help you focus on one stage at a time. That way, you move forward, and you know exactly what to work on next.
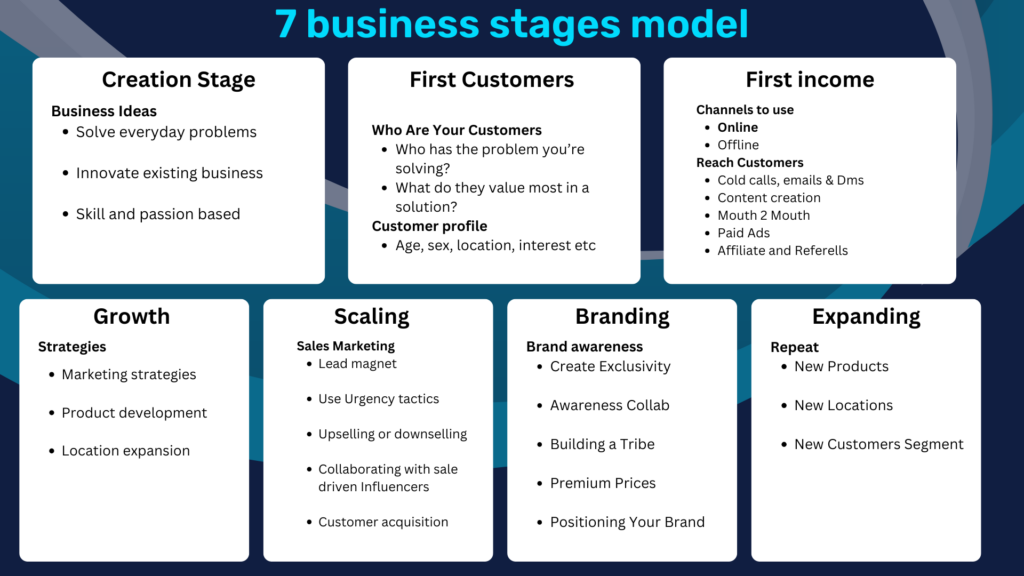
1. Creation: The Start of Your Business
Every business starts with an idea.
This step is about researching and spotting gaps or opportunities in the market.
Usually, a business idea comes in one of three ways:
- Finding Solutions for Everyday Problems: You notice small problems or challenges and create something that solves them.
- Improving or Innovating Existing Solutions: You take what already exists and make it better, faster, or easier.
- Using a Skill or Passion You Have: You turn what you’re good at or what you love into a business that solves a real need.
Your business has to solve a real problem. If it doesn’t fix something, it won’t work.
If you’re selling a physical product, decide whether to:
- Produce it yourself
- Partner with a manufacturer
- Resell an existing product
For service-based businesses, decide whether to:
- Sell to other businesses (B2B)
- Sell directly to individual customers (B2C)
No matter if your business is online or offline, digital marketing is non-negotiable. With 63 percent of the population on social media, that’s likely where your audience will find you, unless you’re targeting rural areas with little connectivity.
As you move forward, things will get clearer. Part of the journey is figuring it out along the way.
Don’t wait for perfection. Start with what you know and adapt as you go.
Just start.
2. First Customer Segment: Finding Your First Buyers
Once you have your product or service idea, the next step is finding your first group of customers.
This is your target audience, the people who will benefit the most from what you offer.
To find them, ask yourself:
- Who has the problem you’re solving?
- What do they care about most when it comes to solving it?
- Where are they hanging out or spending time?
Knowing your first customer segment helps you focus. It guides your marketing and sharpens your messaging.
You need to know who they are, what they do, what they need, and what they care about.
The more specific you get, the easier it becomes to reach and serve them.

There are 5 ways you can reach your customers
There are 3 free ways to reach your customers, but they take time and consistency:
- Cold Calls, Emails, and DMs: Reach out directly to potential customers.
- Content Creation and Personal Brand: Share valuable content and build trust over time.
- Word of Mouth: Let happy customers spread the word for you.
And 2 paid methods that are faster and can bring in your first income stream:
- Paid Advertisement: Run ads to reach a wider audience quickly.
- Referral and Affiliate Programs: Reward others to promote your business.
Your goal here shouldn’t just be getting new customers, but also taking care of the ones you already have.
Keep them satisfied, make them come back, and give them a reason to tell others about you.
3. First Income Stream: Bringing in Revenue
Your focus here is simple:
Add new offers that make sense for your audience,
Increase the value of the customers you already have
At this stage, you’ll experiment with different revenue streams:
- Subscription models for digital services or recurring products.
- One-time sales for physical goods, coaching, or consulting.
- Sponsorships for conferences, events, podcasts, or newsletters.
The goal is to start small. Focus on establishing one reliable income stream before branching out into others.
The question now is, how are you gonna monetize first customers in order to sell your products and services?
Many startups get investments at this stage.
They usually jump into scaling before becoming profitable.
That worked back in the 2000s when no one really knew how to monetize SaaS or digital products.
But today, it’s easier to figure out how to make money by studying what similar businesses are doing.
If you try to scale, build a brand, and expand without a clear path to profit, you’re putting your whole business at risk.
Investors are on a timer. They are not here for the long haul. Their goal is to exit and make money.
Here’s what happens, some businesses rely completely on investor funding just to survive. But when that money dries up, they either downsize or shut down completely.
It doesn’t matter how much you’ve raised or how much pressure you’re under, your focus should always be on your customers.
Build a business that’s profitable first.
4. The growth phase
In the growth stage, you need to plan your business growth strategy. There are 3 ways to approach it, and which one to prioritize first depends on the sector your business is in.
Growth efficiency
This is the stage where you prepare your business for growth.
In the building phase, you’re working in the business, trying to make it profitable and stable except startups.
You’re doing most of the things yourself or with a small team that helps you keep things running.
But in the growth stage, it has to shift. You’re still keeping the foundation solid, but now you need to start working on the business.
That means improving systems, optimizing how things run, and making sure everything can handle more volume.
You also start hiring or partnering with people who focus on growth, agencies, consultants, or team members that are growth hackers
It’s like going from a 5k to a marathon. You need better shoes, more energy, and a real plan to go the distance.
5. Scaling: Handling Larger Demand
Scaling Strategy: Focus on selling more of your current products to more customers.
Startups often scale by pushing their existing product to a wider audience. It’s a way to grow without building something new from scratch.
The marketing strategy at this stage is not about branding. It’s about sales.
Your strategy should always drive revenue. Here’s what to focus on:
- Lead magnet automation
- Urgency tactics
- Upselling or down-selling to let your customers spend more
- Collaborating with sales-driven influencers
- Serving more people without dramatically increasing your costs
To handle the demand, you’ll need to improve your systems, automate as much as you can, and grow your team.
Efficiency and speed matter here more than perfection. Your job is to increase output without letting expenses explode. The goal is to grow profitably by increasing output while keeping expenses in check.
6. Branding: Building a Strong Identity
The more people know about your brand, the more you sell. Increasing visibility is key in this stage.
A fashion business, for example, may focus on brand awareness to position itself as a trend leader and attract a wider audience. Unlike startups that scale first, these businesses build a brand to scale.
While brand personality starts from day one, this is the stage where you’re intentionally building a brand.
Your business needs a strong identity that people recognize and trust.
Create something that reflects your values, your mission, and what makes you different. Branding is more than a logo, it’s how people feel about your business.
The marketing strategy to focus on:
- Create Exclusivity
Limited editions or exclusive access make customers feel special and seen. - Build a Tribe
Build a community around your brand with people who believe in the same values. - Premium Prices
Price your offer to reflect the quality and experience, not just the product. - Position Your Brand
Be clear about who you are and why you matter, so you stand out. - Collaborate with Influencers
Partner with people who already speak to the audience you want to reach.
To build a strong brand, you need consistent messaging, excellent customer service, and a clear image people can connect with.
7. Expanding: Reaching New Markets
Once you’ve scaled and built a brand, it’s time to expand.
Some expansion steps might have already started during earlier stages, especially in the growth phase. If not, now is the time to actively plan how to grow beyond your current setup.
This could mean:
- Entering New Geographic Markets
Reach more people by moving into new regions or countries. - Launching New Products or Services
Offer more to your existing audience by solving new problems. - Targeting a New Customer Segment
Find a different group of people who could benefit from what you offer. - Buying Other Businesses
Expand faster by acquiring companies, entering new markets, reducing competition, or gaining strategic advantages.
Expansion gives you the chance to apply everything you’ve already done, but this time, with experience. You’ve been through the stages, now you can repeat them smarter, faster, and with more confidence.
Conclusion: The Continuous Process
Building a business is a continuous journey.
The key is to start small, grow with intention, and stay adaptable as you face challenges and opportunities along the way.
Whether you’re just starting or already thinking about expansion, this model gives you direction and clarity to build a business that actually lasts.



